The amount of overdue debt in Poland has reached PLN 84.7 billion by the end of December 2024, a figure that could be used to purchase approximately 151,300 apartments of 40 square meters each in the country’s major cities. This staggering amount surpasses the annual cost of the $800+ Program, which stands at PLN 70 billion. According to data from the Register of Debtors BIG InfoMonitor and the BIK credit database, Poles’ unpaid debt increased by nearly PLN 1.2 billion over the past year. Despite the overall increase, the number of unreliable debtors has stabilized, and the rate of debt accumulation has slowed.
The InfoDebt report, compiled using data from BIG InfoMonitor and BIK, serves as a barometer of overdue debt in Poland, categorizing arrears based on age, gender, and region. The latest findings confirm that overdue loans, unpaid rent, fines, court fees, and alimony payments continue to grow. However, the number of individuals struggling with overdue payments has declined. Between December 2023 and December 2024, the number of debtors fell by nearly 129,000 (-4.8%), a significant improvement compared to the previous year’s decrease of only 15,500. The decline in unreliable payers was observed across all age groups.
Despite this improvement, certain demographic groups continue to bear a heavy financial burden. Individuals aged 45-54 and 35-44 have the highest proportions of unreliable debtors, at 11.4% and 10.3%, respectively. In total, the number of unreliable debtors in Poland stands at 2,535,645—equivalent to more than three times the population of Kraków and nearly the combined populations of Łódź and Wrocław.
Financial Struggles and Economic SentimentBIG InfoMonitor President Paweł Szarkowski highlighted that while many Poles managed to improve their financial situation in 2024, a significant number still face economic difficulties. Rising living costs and economic uncertainties contribute to these challenges. According to the “IPSOS Predictions 2025” study, 66% of Poles expect inflation to rise, and 73% anticipate that prices will increase at a faster rate than wages.
A January consumer sentiment survey by CBOS further underscored these concerns. Nearly half of respondents (47%) reported cutting back on spending to meet their essential needs. However, 50% managed to save money despite financial pressures. The average overdue debt per individual increased to over PLN 33,400 in 2024, up from PLN 31,400 the previous year—equivalent to nearly six months’ worth of an average salary.
Slowdown in Debt Growth and Regional DisparitiesAlthough overdue debt continues to rise, the growth rate has slowed. The total amount of arrears increased by PLN 1.2 billion (1.4%) in 2024, compared to a more significant PLN 4.7 billion (6%) rise in 2023. By the end of December 2024, unpaid liabilities recorded in the BIG InfoMonitor Register and BIK database amounted to PLN 84.7 billion.
The Overcome Payments Index of Poles (IZPP), which measures the share of unreliable debtors per 1,000 adults, also saw a decline, falling from 85.4 points in December 2023 to 81.2 points in December 2024. However, the index varies significantly across regions, ranging from 44 to 107, reflecting differing economic conditions across the country.
Regional Debt Trends: East vs. WestRegional disparities in debt repayment remain evident, with eastern Poland faring better than the west. The Podkarpackie Voivodeship had the lowest share of unreliable debtors, with only 44 per 1,000 adults struggling with overdue payments. In contrast, western regions recorded higher numbers, with Lubuskie (107), Zachodniopomorskie (104), and Lower Silesia (103) topping the list.
Only four voivodeships managed to reduce their overall debt: Silesian (-2.1%), Kuyavian-Pomeranian (-1.0%), Małopolska (-0.7%), and Świętokrzyskie (-0.5%). In contrast, regions such as Mazowieckie (4.5%), Zachodniopomorskie (3.5%), and Lubelskie (2.9%) saw the most significant increases in unpaid liabilities. Mazowieckie remains the most indebted region, with PLN 16.7 billion in outstanding payments, followed by Silesia (PLN 9.7 billion) and Lower Silesia (PLN 7.7 billion). The lowest debt levels were recorded in Opole, Świętokrzyskie, and Podlaskie, where overdue liabilities remained below PLN 2 billion.
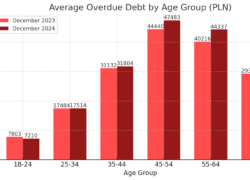
Debt by Age Group: Younger Generations Struggle LessYounger generations exhibit fewer financial arrears compared to older groups. Among 18-24-year-olds, there were fewer than 120,000 unreliable debtors, while the 35-44 age group had nearly 650,000. The youngest debtors also had the lowest average overdue liabilities, standing at PLN 7,210—a decline of PLN 593 from the previous year. In contrast, individuals aged 45-54 held the highest per-person overdue debt, averaging PLN 47,483.
BIG InfoMonitor and BIK data indicate that the most financially burdened group consists of individuals aged 35-54, with over 1.2 million unreliable debtors and total unpaid liabilities nearing PLN 48 billion. However, the most significant increase in overdue debt was observed among those aged 55-64, whose average unpaid debts grew by PLN 4,121 per person.
Biggest Debtors in PolandA small fraction of individuals account for a disproportionately large share of Poland’s overdue debt. The top 1% of unreliable debtors collectively owe PLN 523 million, with their debts increasing by PLN 11.4 million in 2024. The most indebted individual in Poland, a 68-year-old man from the Lubelskie Voivodeship, owes over PLN 92 million.
Conclusion: A Mixed Financial OutlookWhile Poland has seen some improvements in debt repayment, with a declining number of unreliable debtors and a slower rate of debt growth, the overall amount of overdue liabilities remains alarmingly high. Many Poles continue to struggle with financial difficulties, exacerbated by inflation concerns and rising costs of living. Policymakers and financial institutions will need to focus on sustainable economic solutions to prevent deeper financial crises in the future.